Plastic fabrication is the process of designing, producing, and assembling a product composed of plastic material or compounds. Given the enormous range of plastic-based products available today, several plastic fabrication techniques exist. Manufacturers should consider the benefits and drawbacks of each when fabricating specific designs. Plastic fabrication is currently very popular among manufacturers for its flexibility and affordability. It is a resilient and adaptable manufacturing process. Read More…
We are accomplished plastic fabricators. The usability of our products is unmatched. We offer a plethora of secondary services for optional features. All of engineers are extremely thorough when creating these plastics. Your satisfaction is essential to us. You can count on us to give you exactly what you are looking for. Give us a call today to learn more information!
Experts in unique custom plastic extrusion products and complex secondary fabrications, Northland Plastics specializes in custom plastic profile extrusions such as extruded plastic tubing, rigid plastic profiles and flexible plastic profiles. Call Northland Plastics, Inc. for all your extrusion needs.

Thrust Industries is committed to quality in everything it does, from its technical knowledge to its customer service. As a leading plastic fabricator, the entire team at Thrust is devoted to developing high-quality solutions for your business and delivering them exactly when you need them. Thrust has served the needs of customers across the globe for over 3 decades— become one of them today.
At Creative Design and Machining, we specialize in delivering high-quality plastic fabrication solutions that meet the unique needs of our customers across a wide range of industries. We take pride in combining innovative design capabilities with advanced machining techniques to produce components that are both functional and reliable.

More Plastic Fabricator Companies
Types of Plastic Fabricators
Plastic is one of the most versatile and durable materials used in modern manufacturing. Its adaptability and easy customization have made it a core material across industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, electronics, packaging, and consumer products. Plastic fabrication encompasses a diverse range of manufacturing techniques, each designed to meet specific needs in terms of part geometry, production volume, mechanical properties, and cost efficiency. Understanding the different types of plastic fabrication processes and the capabilities of various plastic fabricators is essential for engineers, OEMs, and buyers seeking the right solutions for their projects.
Below, we explore several primary and specialized plastic fabrication methods. By recognizing the strengths and applications of each, you can make more informed decisions about which plastic manufacturing process best aligns with your product requirements and end-use goals.
Plastic Welding
Plastic welding is a fundamental plastic joining method that uses heat, pressure, or a combination of both to fuse multiple thermoplastic workpieces together. Similar in concept to metal welding, this technique is ideal for plastics that cannot be effectively joined with adhesives or mechanical fasteners. Plastic welding is especially valuable for creating strong, leak-proof bonds in products such as storage tanks, pipes, automotive parts, chemical containers, and plastic assemblies that require structural integrity.
There are several plastic welding techniques, each suited to different types of thermoplastics and part geometries:
- Hot Air Welding: Directs heated air to soften and fuse plastic surfaces or filler rods.
- Spin Welding: Rotational friction generates heat at the interface of cylindrical parts, rapidly welding them together.
- Ultrasonic Welding: High-frequency mechanical vibrations create localized heat, allowing for precise, rapid welds on small or intricate components.
- Vibration and High-Frequency Welding: Utilizes mechanical motion or electromagnetic energy to fuse complex or irregular parts.
- Contact Welding: Heated tooling is pressed against the plastic surfaces, melting and bonding them upon cooling.
Each plastic welding technique requires specialized equipment and expertise, and the selection depends on the type of plastic, the part’s design, and the desired bond strength. When evaluating plastic fabricators for welding services, consider their process capabilities, material compatibility, and experience with your specific application.

Plastic Compounding
Plastic compounding is the process of blending two or more polymers or additives to create a custom-engineered plastic with tailored properties. This process is central to the plastics industry, enabling manufacturers to design materials that meet specific criteria for strength, flexibility, color, flame resistance, UV stability, conductivity, and more. Compounding is widely used in automotive, electrical, medical, packaging, and consumer goods manufacturing.
The compounding process typically involves melting base resins, incorporating additives, fillers, pigments, or reinforcements, and homogenizing the mixture using extruders equipped with specialized mixing screws. The resulting compounded plastic can then be pelletized and used in downstream processes such as injection molding, extrusion, or blow molding. Benefits of plastic compounding include:
- Enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties
- Improved processability and product consistency
- Cost savings through material optimization
- The ability to meet stringent regulatory or industry standards
When selecting a plastic fabricator for compounding services, assess their material science expertise, in-house testing and quality control capabilities, and ability to develop custom formulations for your specific product needs.
Plastic Thermoforming
Plastic thermoforming is a popular and cost-effective manufacturing process that transforms flat thermoplastic sheets into three-dimensional shapes by heating them to a pliable temperature and forming them over a mold. This method is widely used to produce packaging, trays, enclosures, panels, automotive interior parts, signage, medical device housings, and more. Thermoforming is valued for its rapid prototyping ability, low tooling costs, and suitability for both low and high production volumes.
There are two main thermoforming processes:
- Vacuum Thermoforming: The heated plastic sheet is draped over a mold, and air is evacuated to pull the material tightly against the mold’s surface, creating the desired shape.
- Pressure Thermoforming: In addition to vacuum, air pressure is applied from above the sheet, enabling the material to capture finer details, sharper corners, and more intricate textures.

Key advantages of thermoforming include fast turnaround, flexibility in design changes, lightweight parts, and efficient use of materials. However, it is best suited for medium to large parts with moderate complexity, as extremely intricate or thick-walled components may require alternative processes such as injection molding. Many plastic fabricators recycle excess trim and scrap, enhancing sustainability and reducing overall costs. When choosing a thermoforming partner, consider their mold design expertise, material selection capabilities, and secondary operations such as trimming, assembly, or printing.
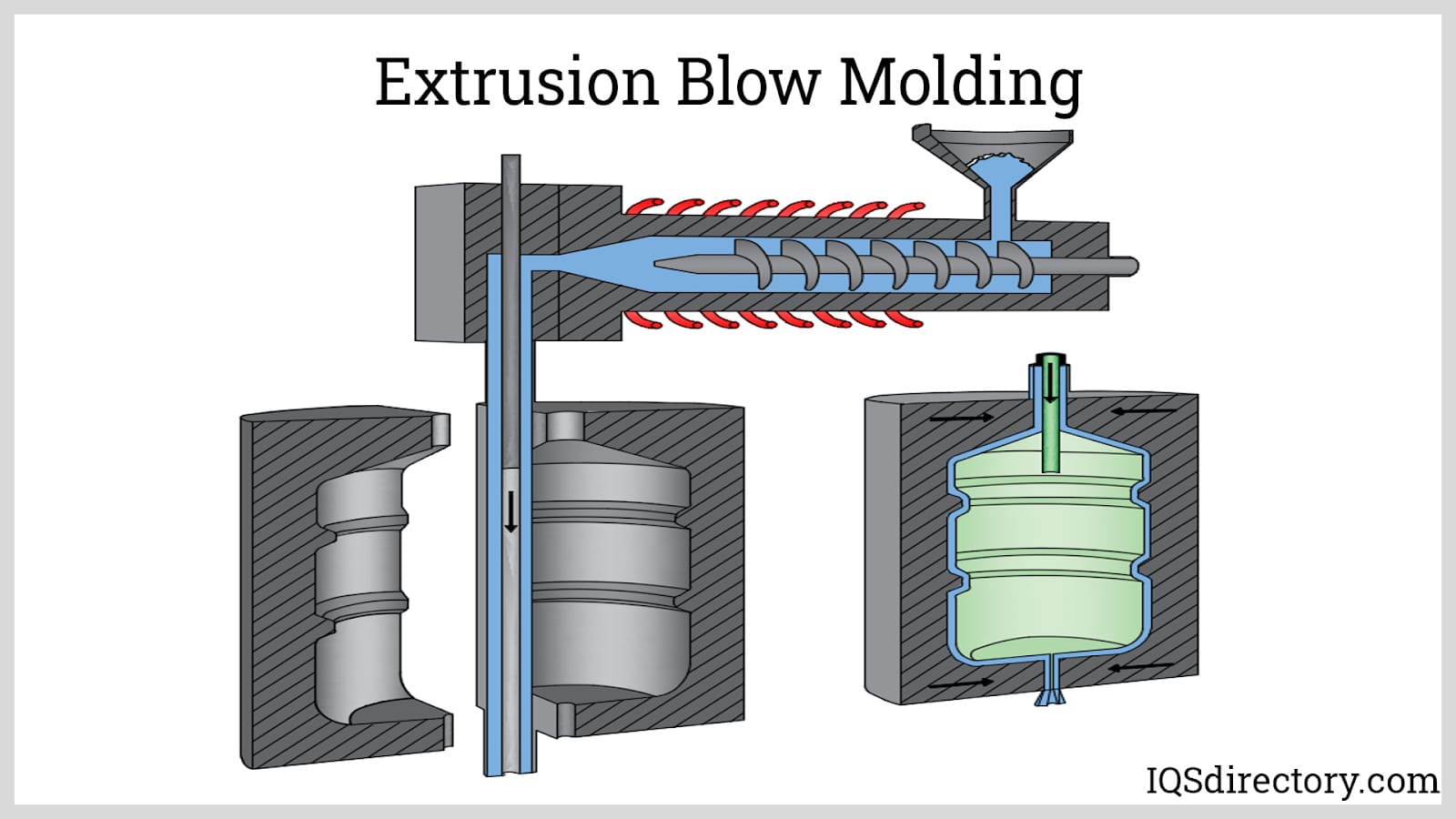
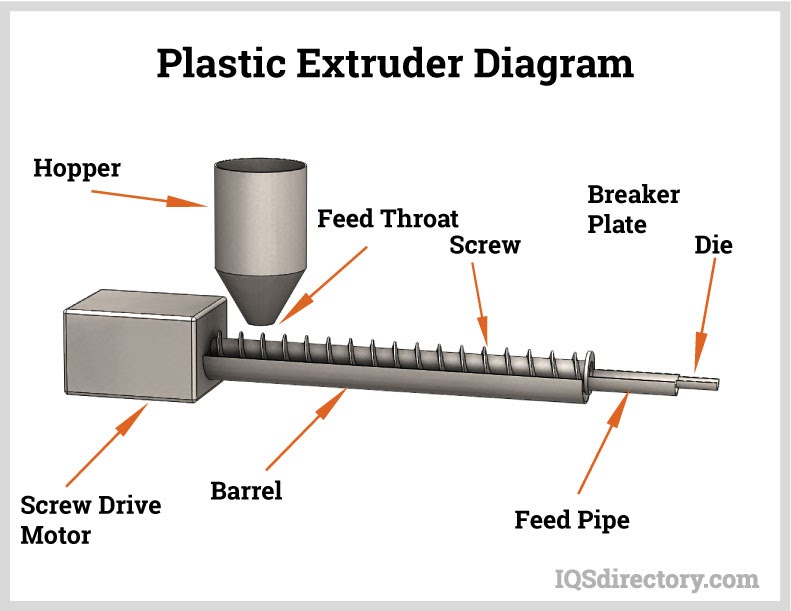
Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process used to create products with consistent cross-sectional profiles, such as pipes, tubes, sheets, films, weatherstripping, wire insulation, and custom profiles. The process begins with feeding plastic pellets or granules into a heated extruder barrel, where a rotating screw mechanism melts and mixes the material. The molten plastic is then forced through a precision-shaped die to produce the desired profile, which is cooled, cut, and finished as needed.
There are several primary extrusion methods:
- Profile Extrusion: Produces custom shapes and structures for construction, automotive, and industrial applications.
- Sheet and Film Extrusion: Creates thin, flat plastic sheeting for packaging, printing, and thermoforming.
- Co-extrusion: Combines multiple materials in a single extrusion run to achieve layered structures with unique performance characteristics.

Extrusion offers high production rates, excellent dimensional consistency, and the ability to incorporate reinforcements, colorants, or functional additives. It is ideal for high-volume manufacturing and products requiring long lengths or continuous rolls. When evaluating plastic extrusion fabricators, review their die design capabilities, downstream processing (such as cutting, drilling, or printing), and material expertise to ensure your project’s needs are met.
Plastic Foaming
Plastic foaming is a specialized fabrication process that creates lightweight, low-density plastic materials with a cellular structure. Foam plastics are used in packaging, cushioning, insulation, flotation devices, automotive parts, construction, and furniture. This method involves introducing a blowing agent—either a chemical that releases gas or a physical agent such as nitrogen or CO2—during plastic processing. The gas forms bubbles within the molten polymer, which expands and solidifies as foam.
Common foamed plastic products include expanded polystyrene (EPS) packaging, polyethylene foam rolls and sheets, polypropylene foam parts, polyurethane cushions, and PVC foams. Additives such as colorants, flame retardants, and UV stabilizers can be incorporated for enhanced performance. Some key benefits of plastic foaming include:
- Significant material weight reduction
- Excellent shock absorption and insulation
- Customization of density and mechanical properties
- Cost-effective manufacturing for high-volume needs

When selecting a plastic fabricator for foam products, consider their experience with your target polymers, available foaming technologies, and ability to customize products for your specific application—whether that’s protective packaging, thermal insulation, or lightweight structural components.
Plastic Lamination
Plastic lamination is a finishing process that applies a protective or decorative plastic film to the surface of another material—such as paper, fabric, wood, or metal—or to plastic substrates themselves. Lamination enhances the durability, moisture resistance, appearance, and chemical stability of products. It is widely used in packaging, signage, labels, flooring, furniture, automotive interiors, and electronics.
There are various lamination methods, including thermal lamination (heat-activated adhesives), pressure-sensitive lamination, and extrusion lamination. The choice depends on the substrate, end-use requirements, and desired finish. Key benefits include:
- Protection against scratches, UV radiation, and contaminants
- Improved visual appeal with gloss, matte, or textured finishes
- Extended product lifespan and reduced maintenance
- Enhanced barrier properties for food or sensitive electronics

When comparing plastic lamination fabricators, evaluate their range of films and adhesives, in-house lamination equipment, and experience with your specific materials and industry standards.
Benefits of Plastic Fabrication
The plastic fabrication industry offers an extensive range of benefits that make it an attractive choice for manufacturers and product designers. The adaptability of plastic manufacturing processes means that customers can achieve solutions tailored for cost, speed, durability, and design flexibility. Some of the most significant advantages of working with plastic fabricators include:
- Ease of Formation: Plastics have relatively low melting points and exceptional malleability compared to metals or ceramics, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and intricate features. This makes plastics ideal for custom components, enclosures, and assemblies that would be costly or impossible to achieve with other materials.
- Rapid Production: Many plastic manufacturing processes—such as injection molding, thermoforming, and extrusion—enable rapid cycle times, short lead times, and high production rates. This translates into faster time-to-market and improved responsiveness to design changes or customer demand.
- Wide Design Flexibility: Plastics can be formed into virtually any shape, thickness, or size, with options for clear, colored, or textured finishes. The diversity of plastic resins and compounding options allows for fine-tuning of strength, flexibility, transparency, and other properties.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Plastic fabrication generally offers lower tooling and material costs than metalworking or glass manufacturing, especially for high-volume runs. Lightweight plastics can also reduce shipping and handling expenses.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: Many plastics are inherently resistant to rust, corrosion, chemicals, and moisture, making them ideal for harsh environments, outdoor applications, and products exposed to cleaning or disinfecting agents.
- Lightweight and Strong: Advanced engineering plastics and composites provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making them suitable for aerospace, automotive, and portable electronic products.
- Sustainability Options: Increasingly, plastic fabricators offer recycled resins, bioplastics, and closed-loop recycling of scrap, supporting eco-friendly and circular economy initiatives.
Common use cases for plastic fabricated products include:
- Custom medical device housings and components
- Automotive interior and exterior trim
- Industrial machine guards and covers
- Consumer product enclosures and packaging
- Architectural panels and signage
- Protective cases, trays, and containers
- Electronics enclosures and components
- Food packaging and display materials
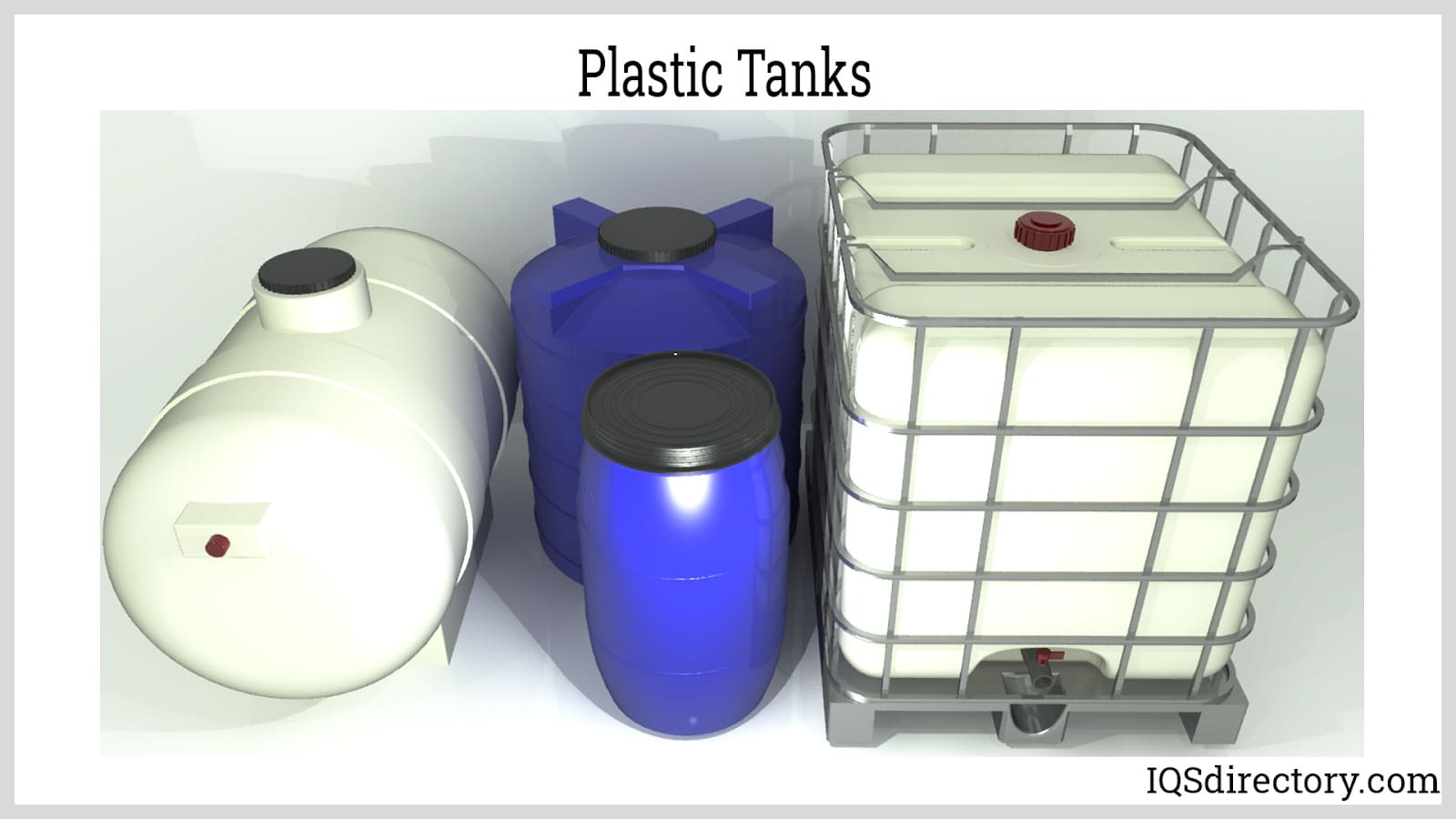
- Water tanks, pipes, and plumbing systems
When evaluating the benefits of plastic fabrication for your application, consider the specific mechanical, thermal, and environmental requirements, as well as industry standards and regulatory compliance needs. Consulting with experienced plastic fabricators can help you select the right resin, fabrication method, and finishing processes to ensure optimal product performance and value.
Choosing the Correct Plastic Fabricator
The decision to select a plastic fabricator is a critical step in any manufacturing project. The right partner will ensure product quality, cost efficiency, and reliable delivery. To achieve the best results, it is essential to compare several companies and evaluate their capabilities, certifications, and industry experience. Our directory of plastic fabricators provides a comprehensive resource to simplify your supplier research and selection process.
Each plastic fabricator listed in our directory features a business profile page highlighting their core competencies, range of services, materials expertise, and production capabilities. You can also find certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485, or industry-specific credentials. The built-in contact form enables you to request more information, discuss technical requirements, or obtain a custom quote directly from the manufacturer.
For more efficient research, review each plastic fabricator business website using our patented website previewer. This tool allows you to quickly compare specializations, previous projects, and value-added services such as prototyping, assembly, or secondary finishing. Once you’ve identified the most promising candidates, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple plastic fabricator companies simultaneously with your project details and requirements.
When evaluating plastic fabricators, ask questions such as:
- What types of plastic fabrication processes and materials do you specialize in?
- Can you provide engineering support for design optimization or material selection?
- What is your experience with my industry’s specific standards or regulatory requirements?
- What are your lead times for prototyping and production?
- Do you offer value-added services such as assembly, decorating, or packaging?
- How do you ensure quality control and consistency across large production runs?
- Can you accommodate custom formulations, colors, or performance requirements?
- Do you offer environmentally sustainable materials or recycling programs?
Choosing the right plastic fabricator involves balancing technical expertise, project management capabilities, cost structure, and communication transparency. By leveraging our directory and resources, you can confidently select a manufacturing partner that aligns with your project goals and delivers exceptional results—from initial concept to finished product.
Frequently Asked Questions About Plastic Fabricators
What industries rely most on plastic fabrication services?
Plastic fabrication is vital for industries including automotive, medical, aerospace, electronics, packaging, industrial equipment, signage, construction, and consumer goods. Each sector values plastics for their design flexibility, lightweight properties, cost efficiency, and ability to meet specific performance criteria.
How do I choose the best plastic fabrication process for my product?
Selecting the right process depends on factors such as part geometry, material requirements, production volume, surface finish, cost constraints, and end-use environment. Consulting with experienced plastic fabricators can help you assess whether injection molding, thermoforming, extrusion, machining, or another method is optimal for your needs.
Are there sustainable and eco-friendly plastic fabrication options?
Yes. Many plastic fabricators now offer recycled, recyclable, or bio-based plastics, as well as closed-loop manufacturing and scrap recycling. Ask potential partners about their commitment to sustainability and ability to support your environmental goals.
What quality standards should plastic fabricators meet?
Look for fabricators with certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485, or sector-specific standards. These indicate robust quality management systems and support consistent, reliable production of high-quality plastic components.
Can a plastic fabricator help with prototyping and design?
Many plastic fabrication companies provide engineering, prototyping, and design-for-manufacturability (DFM) services. Early collaboration can optimize material selection, reduce costs, and speed up product development cycles.
What are typical lead times for custom plastic fabrication?
Lead times vary based on part complexity, process, and order size. Prototyping may take one to three weeks, while full production runs can require several weeks to months, especially if custom tooling or regulatory approvals are needed. Discuss your timeline requirements with fabricators during the quoting process.
Conclusion
The world of plastic fabrication is diverse and rapidly evolving, offering innovative solutions for modern manufacturing challenges. By understanding the major types of plastic fabrication, their unique benefits, and the decision factors for selecting a fabricator, buyers and engineers can ensure successful, high-quality product outcomes. Explore our directory and leverage the latest advances in plastic manufacturing to unlock new possibilities for your next project.







 Die Cutting
Die Cutting Foam Fab
Foam Fab Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services