The term plastic fabrication includes the many industrial processes which produce every conceivable type of plastic product (both stand-alone objects and integral parts). Such plastic creations are used and sold by virtually every modern industry and are among the most in-demand products in the world. Read More…
We are accomplished plastic fabricators. The usability of our products is unmatched. We offer a plethora of secondary services for optional features. All of engineers are extremely thorough when creating these plastics. Your satisfaction is essential to us. You can count on us to give you exactly what you are looking for. Give us a call today to learn more information!
Experts in unique custom plastic extrusion products and complex secondary fabrications, Northland Plastics specializes in custom plastic profile extrusions such as extruded plastic tubing, rigid plastic profiles and flexible plastic profiles. Call Northland Plastics, Inc. for all your extrusion needs.

Thrust Industries is committed to quality in everything it does, from its technical knowledge to its customer service. As a leading plastic fabricator, the entire team at Thrust is devoted to developing high-quality solutions for your business and delivering them exactly when you need them. Thrust has served the needs of customers across the globe for over 3 decades— become one of them today.
At Creative Design and Machining, we specialize in delivering high-quality plastic fabrication solutions that meet the unique needs of our customers across a wide range of industries. We take pride in combining innovative design capabilities with advanced machining techniques to produce components that are both functional and reliable.

More Plastic Fabrication Companies
Plastic, in its broadest sense, refers to any synthetic polymer that mimics the properties of natural resins. In technical terms, a polymer is a molecule made up of extremely long chains, and resins are natural, viscous organic compounds that solidify and are insoluble in water. Plastic fabrication refers specifically to a range of industrial processes that transform plastic resin into finished, functional products for consumer or industrial use. This comprehensive process is typically divided into three main subcategories: design, manufacturing, and assembly.
History of Plastic Fabrication
The development of plastics and plastic fabrication is a remarkable journey that spans centuries, with the definition of “plastic” itself evolving over time. Early civilizations made use of naturally occurring plastic-like materials, such as horn, shellac, and rubber, for thousands of years. However, the birth of modern plastics began in the mid-19th century during the Industrial Revolution—a period that ushered in synthetic chemistry and new manufacturing possibilities.
British inventor Alexander Parkes is credited with creating the first man-made plastic, “Parkesine,” in 1862. Derived from cellulose, Parkesine was first showcased at London’s Great Exhibition. Shortly after, American inventors John Wesley Hyatt and his brother refined this material by adding camphor, resulting in celluloid, a versatile plastic used for items such as combs, photographic film, and billiard balls.
The next major milestone in plastic fabrication was the invention of Bakelite by Belgian-American chemist Leo Baekeland between 1907 and 1909. Made from phenol and formaldehyde, Bakelite was the first fully synthetic plastic and gained widespread use in electrical insulators, radio housings, and kitchenware. Subsequent decades saw the creation of well-known polymers such as polystyrene, polyester, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyethylene—laying the groundwork for today’s advanced plastic manufacturing processes.
The two World Wars accelerated innovation in the plastics industry, with materials such as nylon, acrylic, and PTFE (Teflon) developed for military and industrial applications. After World War II, surplus plastic production found new life in consumer goods, exemplified by the introduction of Tupperware in 1948. Today, plastic fabrication is central to nearly every aspect of modern life, from packaging to aerospace engineering.
Advantages of Plastic Fabrication
The widespread adoption of plastics across industries is primarily due to their inherent advantages over traditional materials such as glass, metal, and wood. Key benefits of plastic fabrication include:
- Versatility: Plastics can be engineered to possess a wide range of properties, enabling manufacturers to produce components and products with varying degrees of flexibility, rigidity, transparency, or color. This makes custom plastic fabrication ideal for industries requiring unique solutions.
- Lightweight and Safe: Compared to metals and glass, plastic materials are significantly lighter, reducing transportation costs and improving safety in applications where weight is critical, such as automotive and aerospace sectors.
- Durability and Resistance: Plastics offer excellent resistance to corrosion, moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, making them suitable for harsh environments and outdoor applications. Their impact resistance often surpasses that of comparable materials.
- Cost-Efficiency: Plastic fabrication processes are generally more cost-effective than those for metals or ceramics, especially for high-volume production. This affordability extends to raw materials, tooling, and manufacturing time.
- Design Flexibility: Complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult or expensive to achieve with metals become feasible with plastics. This is especially apparent in injection molding and 3D printing.
- Electrical Insulation: Many plastics are excellent electrical insulators, making them vital in the electronics and electrical industries.
Despite these benefits, it is important to consider the environmental impact of plastic production and disposal. Certain fabrication methods, such as the “spray up” process, can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like styrene into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and potential health risks. Responsible manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, including recycling plastics and using bio-based resins, to reduce their ecological footprint.
Key Stages of the Plastic Fabrication Process
To answer the question, “How are plastic products made?”—it is essential to understand the stages that make up the plastic fabrication process. These stages are typically divided as follows:
- Design: Involving computer-aided design (CAD), prototyping, and selecting materials based on the intended application and required properties.
- Manufacturing: Transforming raw plastic resin into usable shapes or forms through various molding and forming methods.
- Assembly and Finishing: Combining fabricated parts and applying surface finishes for aesthetics or enhanced performance.
Let’s explore these stages and their associated fabrication methods in detail.
Manufacturing Methods in Plastic Fabrication
Plastic fabrication begins with raw resin, which may arrive as pellets, granules, powder, or flakes. These raw materials are typically derived from petrochemical sources (oil, natural gas, or coal) or, increasingly, from renewable resources (bio-based plastics). Plastics are classified into two main categories based on their behavior upon heating:
- Thermoplastics: Can be melted, reformed, and recycled multiple times (e.g., polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC).
- Thermosets: Harden permanently after curing and cannot be remelted (e.g., epoxies, phenolics).
Raw plastic is often compounded with additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardants, pigments, and fillers to enhance its properties, improve processing, and meet specific performance criteria.
Common Plastic Fabrication Techniques
- Injection Molding: The dominant process in industrial plastic manufacturing, injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a steel or aluminum mold cavity under high pressure. Once cooled, the part is ejected. This method is ideal for mass-production of complex, high-precision parts, such as automotive components, consumer electronics housings, and medical devices. Learn more about injection molding processes & applications.
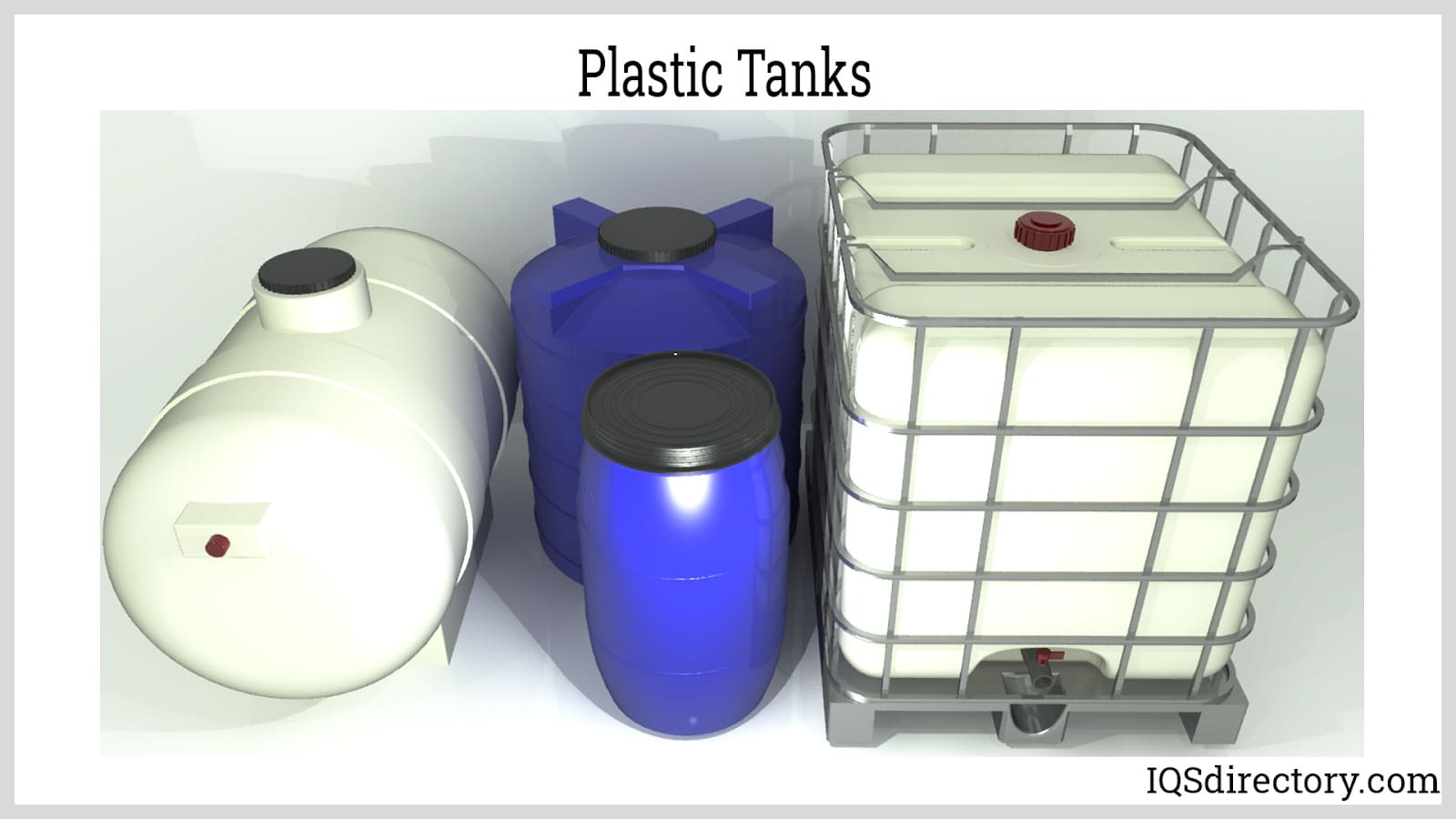
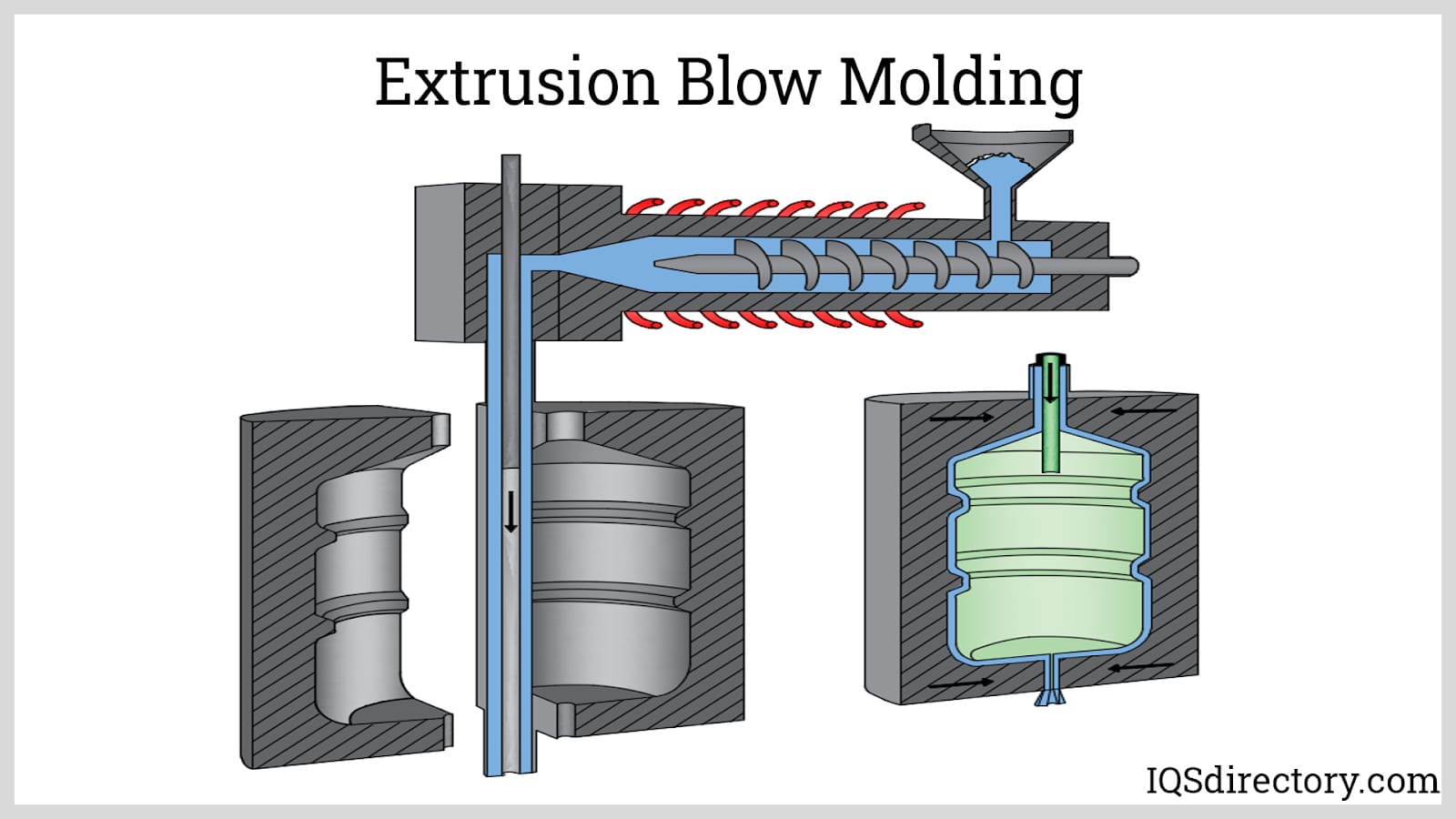
- Blow Molding: This process creates hollow plastic parts, such as bottles, tanks, and containers, by inflating a heated plastic preform within a mold using compressed air. Variants include extrusion blow molding and injection blow molding.
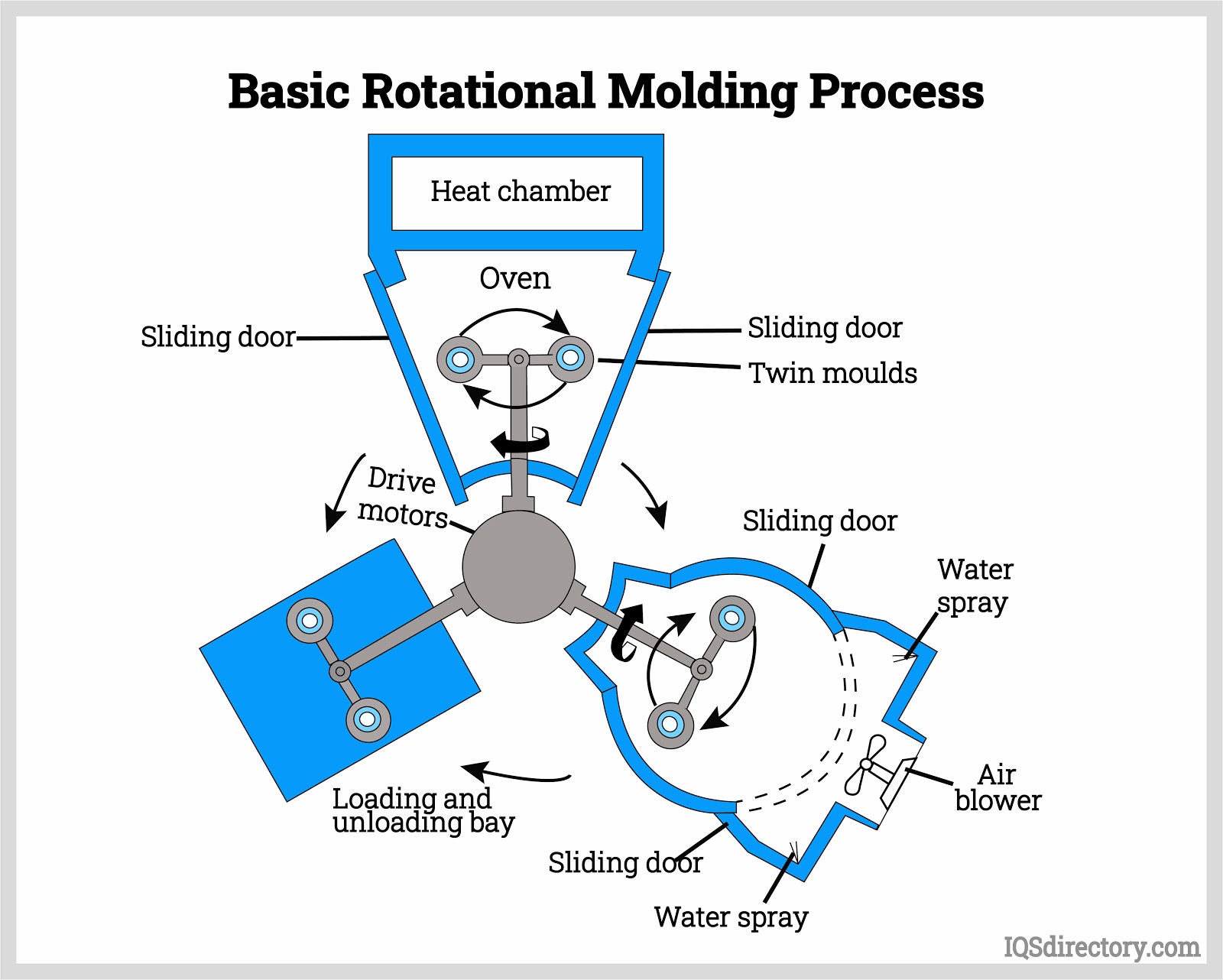
- Rotational Molding (Centrifugal Casting): Used to produce large, hollow items like tanks, playground equipment, and kayaks, this method involves heating plastic resin inside a rotating mold, allowing even distribution and forming of seamless, durable parts.
- Compression Molding: Plastic resin or a sheet molding compound (SMC) is placed in a heated mold cavity, then compressed and cured using hydraulic pressure. Common in automotive parts, appliance housings, and electrical components.
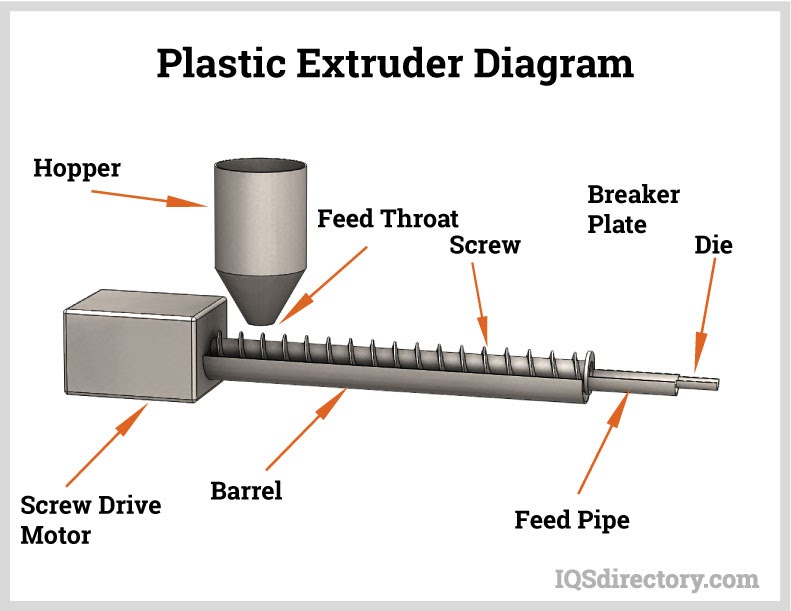
- Extrusion: Plastic resin is melted and forced through a die to produce continuous profiles such as pipes, tubes, sheets, and films. This method is fundamental for plastic extrusion and pultrusion (pulling material through a die).
- Thermoforming and Vacuum Forming: A plastic sheet is heated until pliable, then shaped over a mold using vacuum or pressure. Thermoforming is popular for packaging, trays, and automotive panels.
- Lay-Up Methods: Ideal for reinforced plastic composites, lay-up involves manually or automatically applying resin to layers of fiberglass or carbon fiber in an open mold. Wet and dry lay-up techniques are used based on resin application timing.
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM): Closed-mold technique where resin is injected into a mold containing a fiber preform. RTM is used for high-strength components in automotive, marine, and aerospace markets.
Assembly and Post-Processing in Plastic Fabrication
Once base plastic parts are manufactured, a range of secondary operations may be performed to achieve the desired final product. Common post-processing and assembly methods include:
- Cutting and Machining: Precision shaping of molded or extruded parts using CNC routers, mills, lathes, or laser cutters. These processes are essential for creating custom plastic components with tight tolerances.
- Welding and Joining: Thermoplastics can be joined via plastic welding techniques such as hot plate welding, ultrasonic welding, spin welding, or vibration welding. Adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening (screws, rivets, clips) are also widely used.
- Lamination: Laminating plastic films or sheets onto substrates enhances surface properties such as strength, chemical resistance, or appearance. Film lamination is common in packaging and signage, while resin lamination is used for composite parts.
- Finishing: Techniques such as polishing, buffing, powder coating, painting, silk screening, and pad printing improve surface aesthetics, add branding, or impart functional coatings (e.g., anti-static, UV resistance).
Modern plastic fabrication often incorporates automation and advanced quality assurance systems. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology streamlines production, delivering consistent, high-quality results and reducing human error.
Did you know? Many users search, “What is the difference between injection molding and extrusion?” or “How do I choose the best plastic fabrication process for my product?” Scroll down to our Considerations section for guidance on selecting the right fabrication method.
Applications and Industries Served by Plastic Fabrication
Plastic fabrication is integral to virtually every modern industry, serving countless commercial, industrial, and consumer needs. Major sectors benefitting from custom plastic fabrication and mass-produced plastic parts include:
- Agriculture: Irrigation components, greenhouse panels, and durable containers rely on plastics for weather resistance and longevity.
- Automotive & Transportation: Bumpers, dashboards, fenders, fuel tanks, lighting components, and interior trim are often fabricated from high-performance plastics for weight reduction and safety.
- Construction & Architecture: Pipes, window frames, siding, insulation, and roofing materials leverage the corrosion resistance and flexibility of plastics.
- Electronics & Electrical: Circuit board substrates, insulators, connectors, and enclosures benefit from plastics’ electrical properties and flame retardance.
- Medical & Healthcare: Medical devices, diagnostic equipment, IV bags, syringes, and hygienic packaging are made via precise, contaminant-free plastic fabrication methods.
- Packaging: Food and beverage containers, shrink wrap, blister packs, bottles, and caps are fabricated for safety, durability, and barrier performance.
- Consumer Products & Retail: Toys, sporting goods, household storage solutions, and point-of-purchase displays rely on the customizability and cost-efficiency of plastics.
- Aerospace & Defense: Lightweight, high-strength composite parts fabricated from advanced plastics and reinforced polymers ensure safety and performance under extreme conditions.
- Signage & Display: Acrylic, polycarbonate, and PVC sheets are cut, engraved, and printed for vibrant, weather-resistant signs and displays.
- Industrial Equipment: Tanks, housings, machine guards, gears, bearings, and wear-resistant components are produced using a variety of fabrication methods.
Finished plastic products include everything from storage containers, display racks, enclosures, and tanks to custom-molded parts such as gears, bearings, spacers, seals, O-rings, and electrical insulators. Many of these items demand advanced fabrication techniques to achieve properties like chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and precise tolerances.
Wondering, “Which types of plastics are best for my application?” or “What are the advantages of polypropylene versus polycarbonate?” Visit our comprehensive guide to plastic materials, their properties, and typical use cases.
Key Considerations When Choosing Plastic Fabrication Services
Selecting the right plastic fabrication company or supplier is a crucial decision for any organization seeking durable, cost-effective, and application-specific plastic components. When evaluating plastic fabricators, consider the following factors:
- Product Specifications & Application Requirements: Define the physical dimensions, tolerances, mechanical properties (tensile strength, impact resistance), thermal stability, and chemical compatibility needed for your application. For example, products used in medical or food processing industries must be FDA-compliant, non-toxic, and capable of withstanding regular sterilization.
- Material Selection: Choose between thermoplastics, thermosets, or reinforced composites based on your product’s performance requirements. Commonly used plastics include acrylic, nylon, polyethylene, polycarbonate, polypropylene, polystyrene, and PVC.
- Fabrication Process Suitability: Different fabrication techniques have unique advantages, cycle times, and tooling costs. Injection molding is ideal for high-volume, repeatable parts, while CNC machining or 3D printing may be better suited for low-volume, highly customized components.
- Volume and Budget: Consider the anticipated production volume, lead times, and overall budget. Some methods, such as injection molding, require significant upfront investment in tooling but are cost-effective for large production runs. Others, like CNC machining or vacuum forming, offer flexibility for smaller batches or prototyping.
- Quality Control and Certifications: Verify that the plastic fabricator adheres to industry quality standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 for manufacturing quality systems. For thermoplastics, ISO 306 is relevant. Certifications are particularly important for regulated industries, including medical, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
- Customization Capabilities: Assess whether the supplier offers custom design, prototyping, and engineering support (e.g., CAD, 3D modeling, and simulation). This is critical for unique or complex projects.
- Sustainability Practices: Inquire about the company’s approach to sustainability—do they use recycled resins, support closed-loop systems, or offer eco-friendly materials?
- Lead Times and Logistics: Timely delivery and reliable logistics support are essential, especially for just-in-time manufacturing or supply chain integration.
Looking to find the right plastic fabrication partner? Browse our list of top-rated plastic fabrication companies to compare capabilities, service offerings, and specialties.
How to Choose the Best Plastic Fabricator for Your Project
When engaging with a plastic fabrication supplier, ask the following questions to ensure you’re making an informed decision:
- What experience does the fabricator have with your industry or specific application?
- Can they provide material certifications or compliance documentation?
- What quality assurance processes are in place (e.g., barcoding, Kanban inventory management, in-process inspections)?
- Are design and engineering services available to support prototyping and product development?
- What is their capacity for production scaling, and how flexible are they in accommodating custom orders?
- Do they maintain partnerships with raw material suppliers for better sourcing and pricing?
A reputable plastic fabricator will offer both standard products and custom solutions, leveraging advanced tools like CAD, 3D prototyping, and digital simulation. Many leading companies specialize in specific processes—such as extrusion, injection molding, or CNC machining—enabling them to deliver high-quality, application-specific results.
Standards compliance is another key consideration. The most widely recognized standards in the plastics industry are derived from ISO (International Organization for Standardization) guidelines, ensuring consistent quality and safety.
- ISO 9001:2015: Quality management systems for manufacturing and customer service.
- ISO 306: Specifies methods for determining the heat deflection temperature of thermoplastics.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Additional certifications may be required for medical, aerospace, or automotive parts fabrication.
Frequently Asked Questions About Plastic Fabrication
- What is the difference between thermoplastics and thermosets?
Thermoplastics can be reheated and reshaped multiple times, making them recyclable and suitable for a wide range of applications. Thermosets, once cured, form permanent cross-links and cannot be remelted, offering superior heat resistance and dimensional stability. - What are the most common plastic fabrication techniques?
Injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, rotational molding, compression molding, thermoforming, CNC machining, and 3D printing are among the most prevalent methods. Each technique is chosen based on part geometry, production volume, and material requirements. - How do I select the right plastic material for my project?
Assess the required mechanical, thermal, chemical, and optical properties. Consult with material experts or suppliers who can recommend materials such as acrylic, polycarbonate, nylon, or specialized engineering plastics for your application. - Can plastic fabrication be sustainable?
Yes, many fabricators offer recycled plastics and bio-based resins, as well as closed-loop recycling systems. Inquire about a supplier’s sustainability initiatives and eco-friendly options. - What factors influence the cost of plastic fabrication?
Key factors include material choice, complexity, tooling costs, production volume, finishing requirements, and lead times. Consult with suppliers for detailed quotes and design-for-manufacturing (DFM) recommendations to optimize cost.
Still have questions about plastic fabrication processes, materials, or supplier selection? Contact our team of plastic fabrication experts for personalized guidance.
Conclusion: The Value of Expert Plastic Fabrication
Plastic fabrication is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of products and components that are lighter, stronger, and more versatile than ever before. Whether you are developing a prototype, scaling up to mass production, or seeking a custom-engineered solution, understanding the processes, materials, and supplier capabilities is essential for project success.
By leveraging the expertise of experienced plastic fabricators—who offer advanced design, manufacturing, and assembly services—you can reduce costs, accelerate time to market, and achieve superior product performance. For organizations seeking the latest in custom plastic fabrication, industrial plastic manufacturing, and innovative plastic solutions, partnering with a qualified supplier is the best path forward.
Ready to take the next step? Explore our directory of leading plastic fabrication companies and discover the ideal partner for your next project.




 Die Cutting
Die Cutting Foam Fab
Foam Fab Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services